The second day of the Opinion Festival brought another succession of English-language talks, all of which were insightful in their own way. Here are some things we learned from Saturday’s discussions.
Polarisation is worrying for experts, but Russian minorities are not
The early-afternoon talk ‘Divided we fall, united we stand: is polarisation of societies undermining the security of the Baltic States?’ featured a panel of university academics with an interest in Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, and Ukraine. They discussed how the liberal world order seems, according to some people, to be collapsing, and what might replace it.
Dr. Martins Kaprans, from the University of Latvia, who is also an Adviser to the Latvian Ministry of Culture, said of his own country and its large Russian-speaking community, “The Russophone community in Latvia is becoming more differentiated… There is a clear generation gap in the Russian-speaking community, but also socio-economic. Pro-Kremlin views are still heard very strongly, but there is no truly organised group, so the Kremlin itself finds it very hard to [get traction] among them. The idea of being Latvian is also very strong among the Russian-speakers, and this is one reason why the Russian-speaking community does not pose a threat. Support for some geopolitical claims is still a problem, the in terms of polarisation, it doesn’t have the potential to be antagonistic.” He added that the increased popularity of the KPV.lv party, who have had a late run in the polls as we approach the parliamentary elections, is surprising people.
Dr. Anu Realo, from the University of Warwick and Tartu University, who has been studying social change in Estonia, added, “Estonians and Russian-speakers seem to live in parallel worlds, We don’t seem to have problems, but we don’t really see each other, and that is an issue.”
Continuing, she said, “we don’t like to think of ourselves as a class-based society, but you can see a divide in terms of education and other areas. Maybe it’s not a threat, but I don’t really want to live in a country that allows that [kind of social divide] to develop [without addressing it].”
Kaprans, talking about the potential fortunes in the upcoming elections of Latvia’s Russian Union (now rebranded as simply Union) Party, said, “The political landscape is changing. They have historically been seen as pro-Russian, but they’re doing their best to remodel themselves as social-democratic. How successfully? Not very, according to the polls so far.”
Progressive politics are hard to adopt, and harder to stick to, in the Baltic region
In the same discussion, Dr. Kestutis Girnius, of Vilnius University, had scathing words for his country’s politicians. “It’s not a big stretch to say that government in Lithuania has been incredibly selfish. Lithuania has been run by Social Democrats for 12 years. In that time, not a single progressive thing has been done. They are saving the salaries of the rich and having less to distribute. Whatever the IMF says, Lithuania does, unless the IMF asks for a real-estate or automobile tax, in which case they are just those strangers from Geneva.” Realo added, on Estonia, “there’s still this idea that is you work hard, then you can be successful and look after your family, and what happens in the wider society is not really your concern.”
You don’t know what you’ve got ’til it’s going
The discussion ‘Civil society in Europe: why, who, and how should they be mobilised?’ looked at the question of how important civic activism is in shaping a country’s politics, particularly focusing on the swing towards authoritarianism of countries such as Hungary and Poland, and the general rise of political strongmen around the world. “Democracy has suicidal tendencies,” said Jakub Wygnansky, a Polish sociologist and activist. “Maybe history is moving in circles. Madeleine Albright [the Clinton Administration’s Secretary of State] wrote recently, ‘every century needs its fascism.’ To know the value of democacy, sometimes you need the risk of losing it. We see that politics is cyclical. We thought that institutions would be enough to ensure democracy flourished, but now we see that we need actions too.” He later gave the talk a slogan, “remember nothing depends on you, but act like everything does.”
Andre Wilkens, the German CEO of Offene Gesellschaft, cited the example of his late friend Martin Roth, who announced he would quit “the best job in the world,” as Director of the Victoria and Albert Museum in London, at the end of 2017, due to the changes after Brexit. Wilkens told the audience Roth had said, “if something happens to change the world for the worse, what will I tell people in the future that I did?” “He said, ‘what should I tell my children? That while all this was happening, I put on some exhibitions?'” In answer to the question of what ordinary people can do if they want to hold off the tide of authoritarianism, Wilkens told us, “hold a meeting, to promote an open society. We all have a table and chairs. Then, if you start with something small, you might find that things go to the next level, and you might find yourself doing things you’ve never done before.”
Sometimes, the simple things are all that matters
Local politics can, on occasion, seem concerned about comparative trifles, but one issue that angered a sizeable group of people was the raising of alcohol taxes by the current government in 2017. The result was the ‘Your taxes are driving to Latvia’ campaign, begun, according to Sigrid Solnik of the Estonian Roundtable for Development Cooperation, as a campaign on Facebook between friends, that became a trip to Latvia for 500 people, on their day off on Estonian Independence Day 2018, to demonstrate on social media their distaste for the policy.
Narva is next!
In a discussion about the importance of the European Capital of Culture title, for which Estonian cities and towns Narva, Tartu, and Kuressaare are bidding, the co-ordinator of the Narva campaign, Helen Sildna, as this link shows, gave a compelling case for the city in east Estonia, which has a majority population of Russian-speakers.
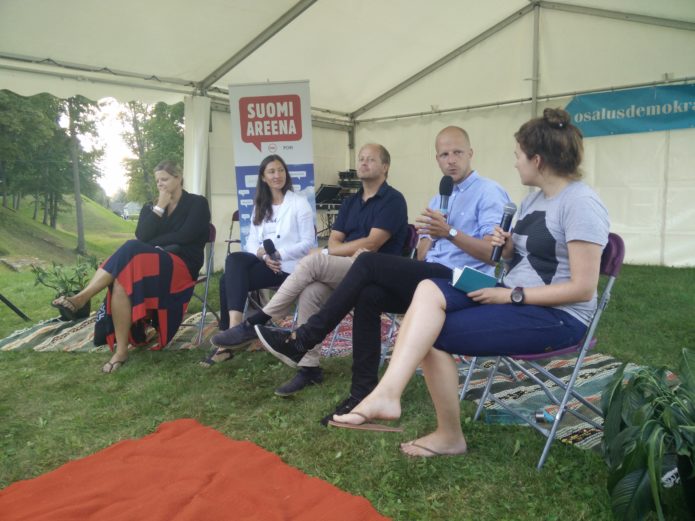





























![IMAG6430[1]](../wp-content/uploads/2015/08/IMAG64301-300x170.jpg)